Welcome to DriverMP!
Cancer is one of the most complex diseases and there are currently more than 100 known types of cancers in humans. The most widely accepted theory is that cancer is mainly caused by genetic mutations. A key issue and major challenge is to distinguish the driver mutations from the massive passengers.
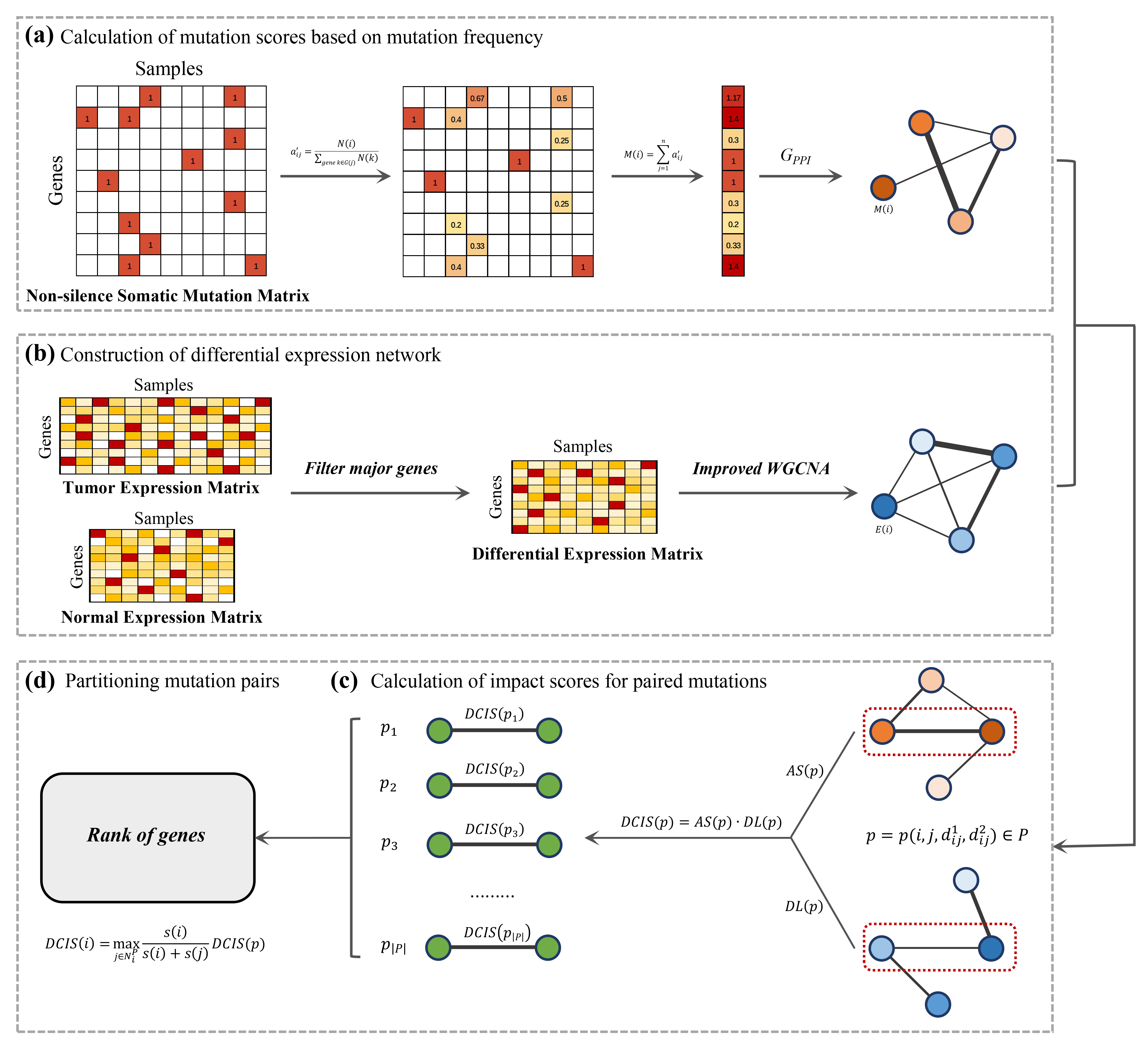
we present a new method termed DriverMP (Multiomics-based Pair driver genes) for effectively prioritizing altered genes on a cancer type level by considering mutation pair genes. It is designed by first applying somatic mutation data, protein-protein interaction network, and differential gene expression data to prioritizing mutation pairs, based on which individual mutated genes are then prioritized. The new approach effectively improves the identification of driver mutations mainly by the following contributions.
Users can use their own data to predict the driver gene for a particular cancer through our online DriverMP webserver . Source code of our server is provided on our Github page https://github.com/LiuYangyangSDU/DriverMP.
At the same time, we provide users with a database of study-validated genes predicted using DriverMP in 10cancer types.
If you think DriverMP is useful, please kindly cite the following paper:
Webserver update:
May, 10th, 2023: the first version of DriverMP server was established.
This work is
openly licensed via CC0 1.0